Investment and economic growth
Investment influences the rate of economic growth because it is a component of aggregate demand (AD) and more importantly influences the productive capacity of the economy. (LRAS)
Readers Question: Discuss the importance of investment in increasing economic growth.
Investment means expenditure on capital spending, e.g. buying new machines, building bigger factories, buying robots to enable automation. (in economics investment does not mean saving money in a bank)
Investment is a component of Aggregate Demand (AD). Therefore, if there is an increase in investment, it will help to boost AD and short-run economic growth.
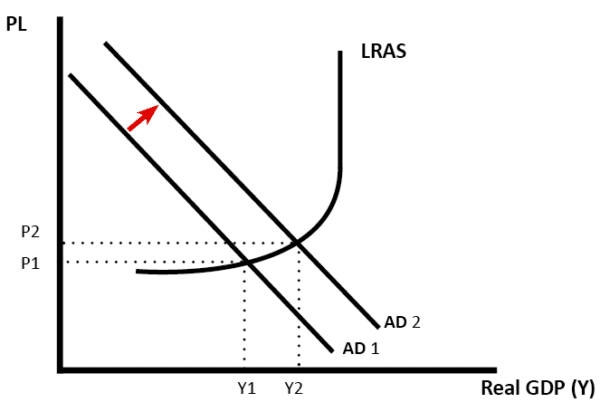
If there is spare capacity, then increased investment and a rise in AD will increase the rate of economic growth.
However, if the economy is close to full capacity, then rising AD will only cause inflation and not an increase in real GDP
However, there are other factors that affect AD apart from investment. For example, if there was a fall in consumer spending or a fall in exports, then a rise in investment may not actually increase AD. Investment is not the biggest component of AD (approx 16%); the biggest component of AD is consumer spending (approx 66%).
Investment and the multiplier effect
If the economy has spare capacity, a rise in investment can also cause a multiplier effect. The initial rise in investment increases economic growth, but if firms gain more sales and profit, they are willing to reinvest this in further investment. Also, households who gain employment from the investment, have more income to spend. Thus an investment of £2 billion could cause a final increase in real GDP of £3 billion. (multiplier effect of 1.5)
Investment and the supply-side of the economy
If investment is effective then it should also increase the productive capacity of the economy. For example, investing in skills and education can increase labour productivity. Investment in new technology and capital can increase productivity and the productive capacity of the economy; this helps to shift long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) to the right. An increase in LRAS is essential for long-term economic growth; it can increase economic growth without inflation. If investment leads to a significant increase in productivity then – it can lead to an increase in the long run trend rate of economic growth. (average sustainable rate of growth
AD/AS diagram showing increase in LRAS and AD
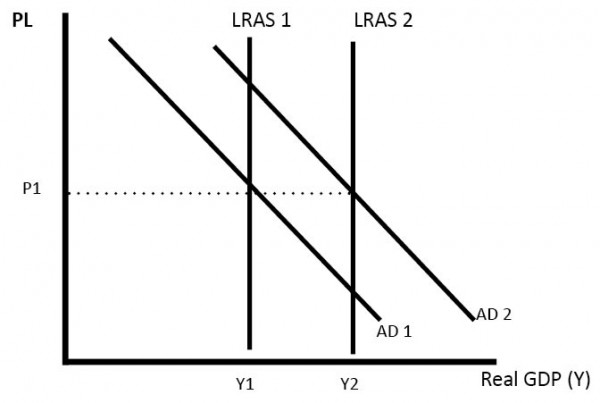
Investment can lead to higher real GDP without inflation.
Evaluation
- It depends on the type of investment. For example, misplaced government investment in improving industrial capacity could be inefficient and fail to increase productivity in the economy. Private sector investment or investment from overseas may be much more effective in actually increasing productivity as private firms have more knowledge about most effective types of investment.
- However, some countries may have supply-constraints in public goods – roads, bridges, infrastructure. These public goods will not be provided fully by the free-market; therefore, it may require government investment to overcome the supply bottlenecks. For example, congestion on the roads is a major constraint for business and economic activity.
- In the long term, investment is important for improving productivity and increasing the competitiveness of an economy. Without investment, an economy could enjoy high levels of consumption, but this creates an unbalanced economy. There will tend to be a current account deficit and little investment in future growth prospects.
How economic growth affects investment
The rate of economic growth also affects the level of investment. Business investment tends to be quite volatile. If businesses see an improvement in economic forecasts, they will increase investment to meet future demand. Therefore, an improvement in the rate of economic growth can cause a substantial rise in investment. But, if there is an economic downturn and a fall in the rate of economic growth, business will cut back on investment.
The accelerator theory states that the level of investment is dependent on the rate of change of economic growth.
However, in addition, to the rate of economic growth, the level of investment also depends on the rate of interest, business confidence, technological progress and government regulations.
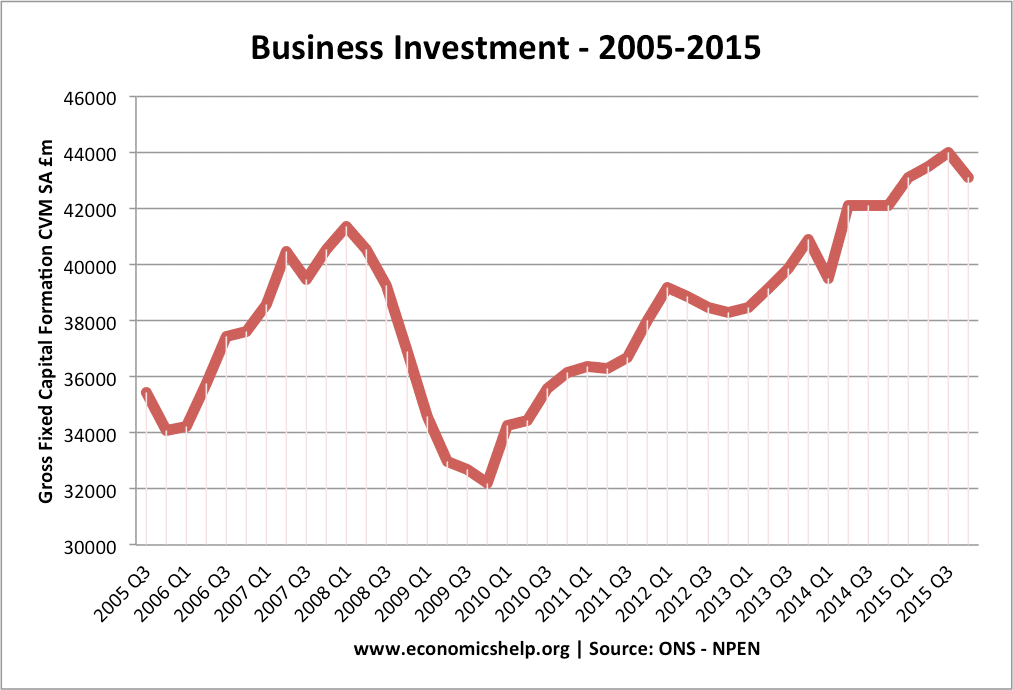
UK Business investment 2005-2015
Business investment fell almost 25% during recession of 2008/09
Economic growth
The fall in investment (caused partly by credit crunch and decline in bank lending) was a significant cause of the recession 2008/09)
Comments
Post a Comment